Buying cheap coins in the crypto world, just like penny stocks, is a trend. But investors needs to understand that shares and cryptocurrencies are very different.
In this article we’ll help you to Discover True Value of a Crypto Token by Using Market Cap & Supply.
Just by borrowing terms like stock price or crypto price and market cap from the stock market does not make them similar.
The dollar price of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies gets a lot of attention and scrutiny. But surprisingly, the price of a digital currency isn’t the best way to assess its value – the market cap is far more important.
What is market cap in crypto?
In its regular usage, market capitalization is the combined value of all of the available shares of a publicly traded company.
We calculate this by multiplying the number of stocks by the price of one stock. So, a company with one million shares each trading at $10 has a market cap of $10 million.
A market cap may also be given for a particular stock exchange (the total value of listed stocks.)
For Bitcoin, the market cap is the number of available coins multiplied by the current price (usually given in dollars.)
Bitcoin is obviously very different to stocks and the figure does not take into account the 4 or so million coins which haven’t been mined yet.
CoinMarketCap calculates the market cap using the circulating supply figures (coins available for use), not the total supply figures (which includes some lost or destroyed coins.)
A general mistake of market cap in crypto is that it is the amount of money invested in that particular coin.
For example, if Coin A’s market cap is 1 billion dollars, it is understood that it is the amount invested in it.
Well, I must say this is a misconception.
Do you think when Bitcoin reached $250 billion in market cap, 250 billion dollars were invested in it?
Of course not.
When market cap increases, the price of every coin increases and one needs to understand there is no new money coming in for the coins that are sitting in yours or anyone else’ pocket.
here is the coin’s market cap formula:
Market Cap = Coin Price x Circulating Coin Supply
Keeping the market cap as constant it is expected that the price of Coin A and Coin B will be high or low.
For example, let us assume that Coin A and Coin B have a market cap of 100 million but Coin A’s circulating supply is 10 million coins while that of Coin B is 100 million coins.
Why does the market cap matter?
The price of one share isn’t a very good indicator of a company’s overall value. It doesn’t tell us anything about the size or profitability of the company as a whole. That’s why it’s useful to look at the market cap.
A company could have a low price per share because there are a lot available and still have a high market cap. And vice versa – a company could have a high price per share and a low market cap. Anything over $10 billion is generally considered a high market cap, which shows the company is profitable and reliable.
In the early days of Bitcoin and cryptocurrencies, the price of one Bitcoin was the dominant metric for measuring its growing value. But as the number of altcoins has increased, market cap has become essential for assessing and comparing the value of a cryptocurrency.
There is a set number of available coins for each cryptocurrency. For Bitcoin, it’s 21 million. For pretty much every altcoin, it’s a different number. This makes it impossible to assess value from the price alone.
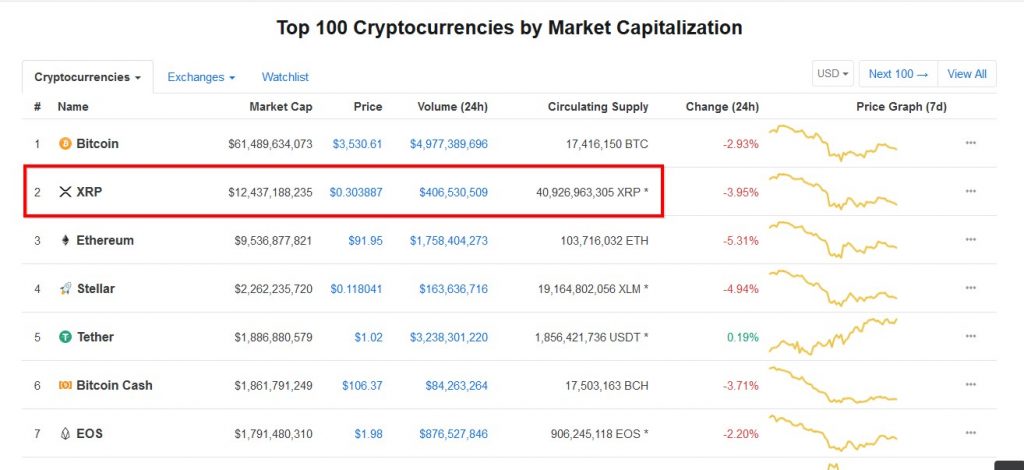
Take XRP, the Ripple network’s currency. It currently costs $1.27 which doesn’t sound impressive compared to Bitcoin- yet it has the third largest market cap of any cryptocurrency. That’s because there are currently almost 39 billion XRP available, compared to under 17 million Bitcoins.
We rank cryptocurrencies by market cap, not by price per coin. This indicates how much fiat currency is invested in each.
If you’re looking to understand the value of a cryptocurrency, be sure to pay attention to the market cap and not the price.
applying coin market cap formula
Now apply the formula:
Coin A’s price would be= ($ 100,000,000/ 10,000,000)= $10
&
Coin B’s price would be= ($ 100,000,000/ 100,000,000)= $1
So you see Coin B has started to appear cheap but one needs to understand and take into account the number of coins in circulation also.
If you ask yourself as to which is a rarer coin to find, the answer is simple – the coin with limited supply.
So, in my opinion, a pricier coin can be cheap because it is very limited in supply whereas a cheap coin can be costly because of its supply volume.
How Does this affect investing?
When we say ‘cheap’ and ‘expensive’, we’re referring to the amount invested in them because this is the key factor to decide how much they can increase:
A ‘cheap’ coin can increase 10x, 100x, 1000x relatively easily
An expensive coin cannot increase so much because it is already expensive
Let’s use an example to explain:
Coin A has a market cap of $10 million
Coin B has a market cap of $100 million
Therefore, the total investments in Coin A are $10 million and the total investments in Coin B are $100 million
For Coin A its market cap to increase 10x, it would simply require that the investments increased to $100 million i.e. a $90 million increase
For Coin B to increase its market cap 10x, it would require that investments increased to $1,000 million ($1 billion) i.e. a $900 million increase
Which is more likely to increase 10x?
Assuming all other things are equal, coin A is much more likely to increase 10x because it requires much less extra investment to do so.
When investing, you always have to consider the risk/reward ratio – coins with lower market caps might have much higher potential returns but they also carry higher associated risk.
A smaller percentage of any portfolio should be committed to the higher risk coins. In other words, larger market cap coins should make up a larger portion of a good portfolio than smaller cap coins.
How To Find Cheap Cryptocurrencies
We’re not talking about fake cheap coins that may cost just 21 cents but aren’t really cheap at all. We’re talking about genuinely cheap coins that have the potential to increase 10x, 100x, maybe even 1000x.
All you have to do is go on the 2nd best website in cryptocurrencies (guess which is number #1) called Coinmarketcap.com which is where we took those screenshots from above from.
It will automatically show you the top 100 coins, ordered by market cap. In other words, ordered from most expensive to least expensive.
As you scroll down the list, you’ll gradually reach the cheaper coins which have the potential to increase a whole lot more than the coins at the top.
Beware: Do not take this as advice for coins you should buy! These coins nearer to the bottom are cheaper for a reason and they’re also a much bigger risk.
The higher the reward, the bigger the risk.
What you need to do is learn how to analyze coins to see which of these cheap coins are undervalued; this is the Warren Buffett method of investing and this is our way too at Crypto Gurus.
Better yet, what if someone analyzed the market and found cheap coins for you? Check out our articles page, hit the ‘Reviews’ tab and you can see some of our research on the most undervalued coins in the market right now!
Now that you guys know what a cheap cryptocurrency actually is – one with a low market cap, not necessarily a low price – let’s move on to what market cap actually means.
bottom line
The original formulas of price and market cap I told you about is a fallacy. There is no concrete way of proving that the formula gives you the correct picture at all times.
If the token supply is 1 million and market cap is $1 million you don’t need $1 million to double the token price. It is a myth. It can happen with $10,000 itself or it might not happen even with $2 million.
And the total amount of money invested in a coin is not the market cap.
Everything is determined by price and price is determined by various visible & invisible factors.
And as a good rule of thumb, 10-150 million token or coin supply is considered healthy for a crypto project. Beyond that, it doesn’t make much sense to me.
Remember this and don’t fall for other concepts as most of them are assumptions.








